Keratin is a protein that aids in the structural maintenance of hair, nails, skin, and the lining of internal organs. Certain nutrients aid in the production of keratin.
This article looks at the benefits of keratin and lists some food sources that may help maintain healthy levels of keratin in the body.
What Is Keratin?
A specific type of non-living protein, keratin makes up our skin, hair and nails. Keratin is produced from living skin cells in the body and is found in our glands and the lining of our organs as well.
Considered a protective protein, keratin provides resilience and strength to cells from mild trauma that includes rubbing or scratching.
Derived from the horns, wools and feathers of different animals, it is widely used in hair cosmetics as one of the key ingredients. Many believe that keratin supplements, treatments and products help hair look healthier and can strengthen the hair’s structural building block.
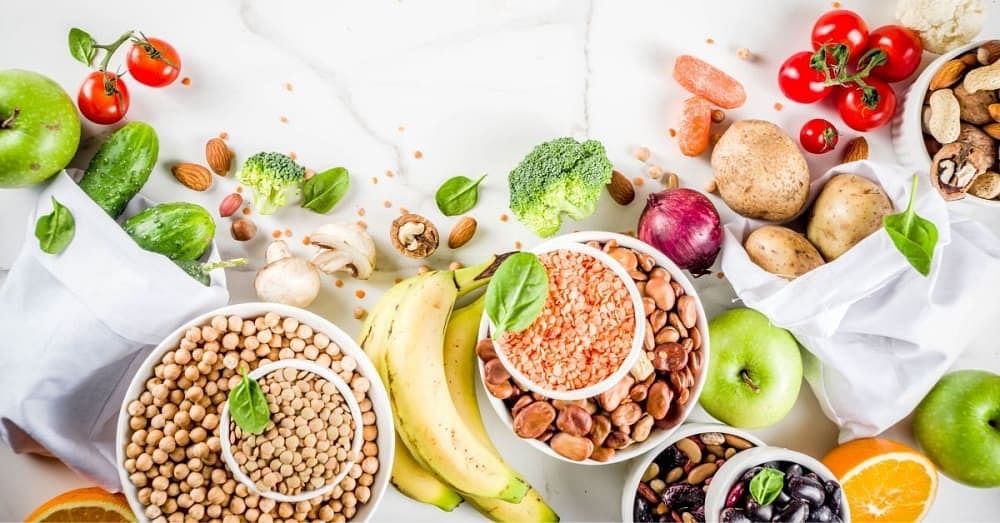
Keratin Rich Foods
Keratin protein is not only important for healthy hair, but it is also responsible for the repair and growth of ligaments, certain tissues, bones, muscles, skin, and beyond.
That is why it is essential to include keratin-rich food in the diet that helps boost keratin levels along with other minerals and vitamins.
Read on to learn about the most popular keratin-rich foods.
1. Eggs
One large egg contains not just protein but other nutrients, including calcium, vitamin A, selenium, vitamin B12, and riboflavin. Moreover, one cooked egg is equipped with 10 mcg of biotin, an important nutrient involved in keratin synthesis.
2. Onions
Onions are known for boosting keratin levels as they contain N-acetylcysteine, a plant-based antioxidant. It gets converted into L-cysteine, a component of keratin made up of amino acids. Moreover, onions are also enriched with folates that help maintain healthy hair.
3. Salmon
Enriched with proteins, omega-3 fatty acids, and biotin, salmon is a wonderful source of keratin. It prevents hair loss, promotes hair density, and improves hair growth.
4. Sweet Potatoes
A powerhouse of health and taste, sweet potatoes contain provitamin A named carotenoids-beta carotene. When consumed, it transforms into vitamin A in the body and produces keratin, leading to healthy hair.
5. Sunflower Seeds
Healthy, tasty and savoury, sunflower seeds boost keratin production, making hair healthy and strong. In addition, sunflower seeds also contain copper, selenium, vitamin E, and pantothenic acid.
6. Garlic
Garlic, equipped with N-acetylcysteine, plant-based antioxidants, protects hair cells from harmful sun damage and promotes healthy hair. When consumed, it gets transformed into L-cysteine, an amino acid that is found in keratin.
Garlic also contains vitamins C and B6, manganese and other essential nutrients.
7. Kale
A highly nutritious green veggie, kale contains provitamin A, which gets transformed into vitamin A which is essential for the synthesis of keratin. It is also enriched with vitamin C that boosts collagen production, helping the skin stay healthy and elastic.
8. Carrots
Enriched with provitamin A, carrots promote healthy hair, nails and skin.
9. Mangoes
Enriched with vitamin C, mango supports keratin synthesis. Also high in provitamin A and several other essential nutrients, including folate, mangoes offer many other benefits besides hair health.
Potential Benefits of Keratin-rich Foods
Being a building block of the body, including hair, there are plenty of benefits of keratin-rich foods:
- Keratin-rich foods help strengthen muscles, tissues and bones by reducing damage from friction.
- Foods rich in keratin help enhance the elasticity of skin and ligaments.
- Keratin plays an important role in maintaining hair health by preventing hair loss. It also boosts the resilience and elasticity of hair.
- Keratin-rich foods help maintain eye health. In addition, keratin regulates cell size and allows cells to grow and heal wounds.
How to Increase Keratin in Hair Naturally?
Keratin deficiency can lead to sagging skin, hair loss and nail breakage. However, you can increase keratin in hair naturally by following these tips:
1. Integrate Keratin-rich Food into the Diet
Keratin is found in many vegetables naturally. They include kale, onions, garlic, broccoli, and leeks. Other good sources of keratin include fish, low-fat milk, yogurt, and liver. Including these foods in your meal is a great way to increase keratin in your hair naturally.
2. Intake of Protein-rich Diet
A range of high-protein foods also helps build keratin. They include red meat, chicken, eggs, yogurt, milk, pork, and fish. As far as plant-based food sources of keratin are concerned, they include beans, nuts, nut butter, and quinoa.
3. Focus on Biotin-rich Diet
Biotin too boosts keratin production by metabolizing amino acids to strengthen hair and nails. A few good sources of biotin are whole grains, eggs (with the yolk), bananas, and a variety of nuts like walnuts, peanuts, pecans, almonds, and more.
A few vegetables are also a good source of biotin, including beans, mushrooms, cauliflower, blackeyed peas, and soybeans.
4. Include Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Intake of omega-3 fatty acids also helps the body make keratin. A few good sources of omega-3 fatty acids include salmon, trout, tuna, mackerel, herring and sardines. However, it is recommended for pregnant women to avoid mackerel fish containing high levels of mercury.
5. Increase the Intake of Vitamin C
To make keratin, the body needs vitamin C. A few good sources of vitamin C include:
- Citrus fruits like grapefruits and oranges
- Tropical fruits like kiwi, mango, pineapple, papaya, cantaloupes, and watermelons
- Different kinds of berries such as strawberries, blackberries, blueberries, cranberries, raspberries and more
- Vegetables such as cauliflower, broccoli, brussel sprouts, tomatoes, potatoes, and peppers
- Leafy green vegetables like spinach, turnip greens and cabbage
6. Include Cysteine in Diet
Cysteine, when consumed, gets transformed into keratin. Foods rich in cysteine include pork, eggs, milk, and seeds. Of these, eggs are considered to be the best source of cysteine, being pocket-friendly and easily available.
7. Use Keratin-based Hair Products
Using hair products that contain keratin may help build up the protein in the hair over time. This, in turn, makes hair softer and smoother. A few keratin-based hair product types include keratin shampoos, styling products and keratin-based conditioners.
You can also use hair products enriched with vitamin B5, zinc, iron, vitamin E, and copper. These nutrients can boost keratin production in hair.
8. Avoid Extreme Use of Hair Styling Products
Using an electric hair straightener and other styling tools can damage the structure of the keratin fibres in the hair. So avoid doing that.
9. Avoid Bleaching Hair
Bleaching hair tends to damage the keratin in the hair cuticles. Gentle dye is fine, but if you want healthy and strong hair, you must avoid hair bleaching.
10. Protect Hair from Sun Damage
Strong sun rays are no less harmful than bleach on hair and hence damage keratin. Light-colored and fine hairs are especially vulnerable to the damage caused by the sun.
Thus, whenever it is required for you to step out in the sun, cover your head with a scarf or a hat to protect your hair from sun damage.
11. Rinse Hair Properly after Swimming
If you swim often, you must rinse your hair thoroughly after every session. A swimming pool typically contains a higher amount of chlorine that dries hair and damages keratin.
Cysteine Vs Keratin
The main difference between cysteine and keratin is that cysteine is free from cancer-causing chemicals like formaldehyde and other harsh chemicals, whereas keratin does contain them.
Therefore, cysteine treatment is safer for pregnant women and children above 12 years. However, cysteine is more expensive. Not only that, it has less longevity. Nevertheless, both cysteine and keratin-treated hair needs to be maintained and well-looked after to get the most benefits.
Is Keratin Treatment Good for Hair?
Yes, Keratin treatment is good for hair. It is used for straightening hair as it adds extra keratin to hair. This process is used to enhance hair shine, reduce frizz and strengthen hair. However, keratin treatment comes with a few undesired side effects as well.
The biggest side effect of this treatment involves the formaldehyde compound that may lead to headaches, nausea, vomiting, sore throat, dizziness, chest pain, eye irritation, vomiting, coughing, rash and more.
Formaldehyde is a harsh cancer-causing agent. Thus, the side effects are not only experienced by the person who undergoes this treatment but also by the hair stylist who provides it.
As far as the benefits of keratin treatment are concerned, it smoothes the hair shafts, resulting in shinier and silky hair. Keratin treatment also straightens hair, smoothens curls, and strengthens strands by making them less prone to wear-and-tear and breakage.
Summing Up on Keratin Rich Foods
Keratin is essential for not just strong, smooth and shiny hair but also healthy skin and nails. Therefore, it is important to boost keratin production in the body. Though keratin can be added to hair through keratin treatment, it has disadvantages.
Therefore, it is recommended to add keratin naturally to the body by making keratin-rich foods a part of your everyday diet. This will help you avoid a range of disorders not just related to hair but skin as well.
References
Priya Nimish Deo, January 2018; Pathophysiology of keratinization - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5917548/
Patel D.P., A Review of the Use of Biotin for Hair Loss - https://www.karger.com/Article/FullText/462981
Wen-Ling Shih, May 2018; Antioxidant activity and leukemia initiation prevention in vitro and in vivo by N-acetyl-L-cysteine - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6036344/
Hans Törmä, Regulation of keratin expression by retinoids - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3219164/
Emily L. Guo, Jaunary 2017; Diet and hair loss: effects of nutrient deficiency and supplement use - https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5315033/