Fungal acne is a common skin condition due to the inflammation of hair follicles. It occurs because of the overgrowth of Malassezia yeasts, especially Malassezia furfur, which is present abundantly.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the clinical features, causes, diagnostic methods, and fungal acne treatment options available for fungal acne.
What is Fungal Acne?
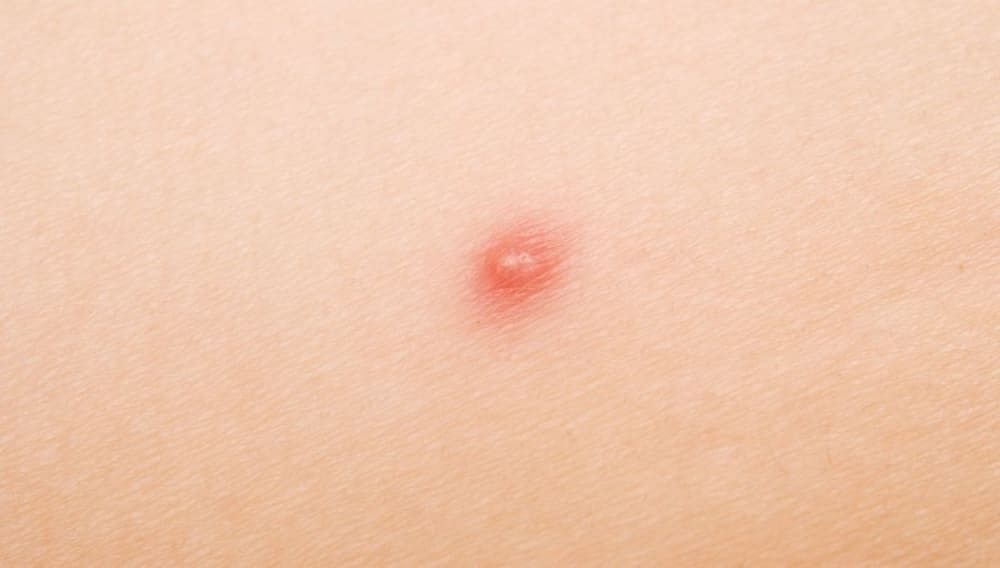
It manifests as small, itchy papules or pustules on the skin. It primarily occurs on the face, neck, and upper trunk. Proper identification and diagnosis are essential to implement effective management strategies.
Managing fungal acne includes specific antifungal agents and lifestyle modifications to alleviate symptoms and prevent recurrences.
How do I know if I have Fungal Acne?
Evaluating your skin’s condition, clinical features, and characteristics is essential to determine if you have fungal pimples or acne. Fungal acne symptoms include:
1) Tiny, uniform pustules: Fungal acne typically presents as small, raised bumps on the skin. These lesions are often uniform, ranging from 1 to 2 millimetres in diameter.
2) Itchy or pruritic lesions: Fungal acne lesions may cause itching or a sensation of discomfort, leading to scratching or rubbing of the affected areas.
3) Presence of white or yellowish heads: The bumps associated with fungal acne contain a white or yellowish substance, resembling traditional acne that looks like whiteheads.
4) Lesions clustering: Fungal acne lesions cluster in specific areas; these include the forehead, jawline, chest, or back. These regions typically have a higher concentration of sebaceous glands.
5) Lack of improvement with traditional acne treatments: It could be a sign of fungal acne if you have been using common acne treatments, such as benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid, without significant improvement.
6) Worsening in humid or sweaty conditions: Fungal acne lesions often exacerbate in hot, humid, or sweaty environments, as moisture and heat contribute to the growth of Malassezia yeasts.
If you suspect you may have fungal acne, it is advisable to consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis. A precise diagnosis will guide appropriate treatment and management strategies tailored to your needs.
Also Read: How to Cure Fungal Infection on Skin Naturally: 10 Proven Remedies
Who might get Fungal Acne?
Fungal acne can affect individuals of any age, gender, or ethnicity. Sources show that the following individuals are more likely to develop fungal acne:
1) Adolescents and young adults: Fungal acne commonly affects teenagers and young adults, as hormonal changes during puberty can increase sebum production, creating an environment conducive to the growth of Malassezia yeasts.
2) People with oily or acne-prone skin: Excessive sebum production provides a favorable environment for Malassezia yeasts to thrive, making individuals with oily or acne-prone skin more susceptible to fungal acne.
3) Individuals living in hot and humid climates: Fungal acne tends to be more prevalent in regions with warm and humid weather. The increased moisture and humidity facilitate the growth of Malassezia yeasts, contributing to the development of fungal acne.
4) Individuals with compromised immune systems: People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, or organ transplant recipients, have a higher risk of developing fungal acne. The immune system plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance of microorganisms on the skin.
5) Individuals who frequently wear occlusive clothing: Tight-fitting or non-breathable clothing can trap moisture and heat on the skin, creating an environment suitable for the growth of Malassezia yeasts and increasing the likelihood of fungal acne.
Fungal Acne Causes
1) Malassezia overgrowth: Fungal acne arises primarily due to an overgrowth of Malassezia yeasts, particularly Malassezia furfur. These lipophilic yeasts naturally inhabit the skin and thrive in areas rich in sebaceous glands, such as the face, upper trunk, and neck.
2) Sebum production: Excessive sebum production provides an ideal environment for Malassezia yeasts to flourish. The yeasts metabolise the triglycerides present in sebum, leading to the release of fatty acids. This triggers an inflammatory response within the hair follicles.
3) Hot and humid climates: Fungal acne is more prevalent in warm and humid environments. Increased moisture levels contribute to the proliferation of Malassezia yeasts and the subsequent development of acne-like lesions.
4) Occlusive clothing: Wearing a tight or non-breathable dress can create a humid microenvironment on the skin, promoting the growth of Malassezia yeasts and exacerbating fungal acne.
5) Prolonged use of topical corticosteroids: The application of corticosteroid-containing creams or ointments on the affected areas can disrupt the balance of the skin microbiome and lead to the overgrowth of Malassezia yeasts, triggering fungal acne.
6) Weakened immune system: Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as HIV/AIDS, organ transplant recipients, or undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, are more susceptible to developing fungal acne.
7) Certain medications: Oral corticosteroids, antibiotics, or immunosuppressants can disrupt the normal flora on the skin and increase the risk of fungal acne.
It is important to note that fungal acne causes may interact and vary among individuals, contributing to the development and persistence of fungal acne.
Also Read: Fight acne, pimples, and blackheads with Clinmiskin
Fungal Acne Symptoms
Fungal acne exhibits distinct symptoms that differentiate it from traditional bacterial acne. The following are common fungal acne symptoms:
- Tiny, round pimples
- Pinkish or reddish pimples with a whitehead
- Swelling and redness around the pimple
- Irritation
- Acne-like breakouts
- Occasional tingling and stinging sensation
- Acne in groups
It is important to note that the symptoms of fungal acne can vary among individuals. If you suspect you may have fungal acne, it is advisable to consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis and tailored treatment plan. A dermatologist can assess your symptoms, conduct a physical examination, and recommend appropriate management strategies to alleviate the condition.
What's The Difference Between Fungal Acne And Regular Acne?
Distinguishing between fungal and regular acne is crucial for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. The key differences between these two conditions:
Fungal acne:
Fungal acne, also known as pityrosporum folliculitis or malassezia folliculitis, is caused by an overgrowth of Malassezia yeasts, primarily Malassezia furfur. These yeasts naturally inhabit the skin and thrive in areas rich in sebaceous glands.
Regular Acne:
Acne vulgaris is primarily triggered by the bacteria Propionibacterium acnes, which colonies the hair follicles and sebaceous glands. Factors like excess sebum production, hormonal changes, and inflammation contribute to the development of regular acne.
1) Lesion Characteristics:
- Fungal Acne: Fungal acne lesions typically manifest as small, uniform papules or pustules on the skin. These lesions are often similar in size (1-2 millimeters) and lack the presence of blackheads or comedones.
- Regular Acne: Regular acne lesions include blackheads (open comedones), whiteheads (closed comedones), papules, pustules, nodules, and cysts. Blackheads and whiteheads are common in regular acne, along with inflammatory lesions.
2) Itching and Discomfort:
- Fungal Acne: Fungal acne lesions are often associated with itching or pruritus, which may lead to scratching or rubbing the affected areas.
- Regular Acne: Regular acne lesions typically do not cause significant itching unless there is concurrent inflammation or infection.
3) Response to Treatment:
- Fungal Acne: Fungal acne may not improve with traditional acne treatments, such as benzoyl peroxide or salicylic acid-based products. Instead, antifungal medications or topical antifungal creams are usually effective in resolving fungal acne.
- Regular Acne: Regular acne responds well to conventional acne treatments, including topical therapies (e.g., benzoyl peroxide, retinoids) and oral medications (e.g., antibiotics, hormonal therapies).
Understanding these differences is essential to guide appropriate management strategies. If there is uncertainty regarding the diagnosis, consult a dermatologist for accurate identification and personalised treatment of the specific acne type.
Also Read: Acne-Prone Skin: What is it, Causes, How To Take Care of It!
Fungal Acne On Face
Having flawless and healthy-looking skin is something many of us strive for. Various skin conditions can disrupt our quest for the perfect complexion. One such condition is fungal acne on the face, a pesky and misunderstood problem affecting countless individuals worldwide. If you're struggling with fungal acne on your face, don't worry – you're not alone. Here is a sneak peek at your worries-
- Oral antifungal medication: One of the best products for fungal acne on the face is these medications that kill or inhibit the growth of fungal cells. Azoles, such as ketoconazole, are commonly used.
- Prescription topical antifungal creams: If over-the-counter products don't work, stronger topical medications like ketoconazole 2% can be applied twice daily for 2-3 weeks to reduce yeast overgrowth.
- Diet adjustments: Avoid yeast-promoting foods like refined sugar and white flour, while incorporating fruits, vegetables, grains, and lean meats can improve the skin.
- Antifungal shampoo or body wash: These products slow down fungal growth. opt for Selsun Blue.
- Oil-free moisturiser: These moisturisers hydrate the skin without adding more oil that can clog hair follicles.
Also Read: Neem Benefits For Acne
Fungal Acne Forehead
Fungal acne forehead is a skin condition caused by an overgrowth of the fungus Malassezia. The yeast forehead bumps appear as small, itchy bumps resembling acne. Factors like sweat, oily skin, humidity, and certain skincare products trigger the nodes. Treatment options include oral antifungal medications, which kill or inhibit fungal cells, and prescription topical antifungal creams like ketoconazole. Try making diet adjustments like reducing the intake of yeast-promoting foods. Antifungal shampoos or body washes can slow fungal growth, while oil-free moisturisers can hydrate the skin without adding excess oil. Seeking medical advice is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Fungal Folliculitis
Fungal folliculitis is a skin condition characterised by inflammation and infection of hair follicles caused by fungal organisms. It typically appears as small, red bumps or pimples with surrounding redness and tenderness. The leading cause is the overgrowth of fungi, such as yeast, on the skin. Factors like hot and humid environments, excessive sweating, tight clothing, and compromised immune systems can increase the risk. Treatment options include antifungal creams, oral antifungal medications, and proper hygiene practices. Avoid tight dress, keeping the affected area clean and dry, and using antifungal shampoos can help prevent recurrence.
How is fungal acne diagnosed?
Fungal acne is diagnosed through a visual examination and medical history. A dermatologist may take a skin sample or perform a skin scraping to confirm the presence of fungal organisms under a microscope.
How is fungal acne treated?
There are many ways to treat fungal acne. The options include:
- Antifungal Topical Medications: Over-the-counter or prescription antifungal creams, lotions, or gels containing ingredients like ketoconazole or pyrithione zinc can be applied directly to the affected areas.
- Oral Antifungal Medications: In more severe cases, healthcare professionals prescribe oral antifungal medications to combat the fungal overgrowth from within.
- Adjusting Skincare Routine: Avoid using comedogenic products and opt for non-comedogenic, oil-free skincare products to prevent clogging of hair follicles.
- Maintaining Good Hygiene: Keep the affected area clean and dry, gently cleanse the face twice daily, and avoid excessive scrubbing or harsh exfoliation.
- Use Antifungal Shampoos: Antifungal shampoos contain ingredients like ketoconazole or selenium sulphide. They reduce fungal overgrowth.
- Lifestyle Changes: Avoid excessive sweating, wear breathable fabrics, and make dietary adjustments to reduce yeast-promoting foods intakes like refined sugars and white flour.
- Follow-up Care: Stick to the treatment regimen as prescribed. Follow up with your healthcare provider to monitor progress.
Also Read: What's The Difference Between Acne And Pimples?
FAQs
How Do I Get Rid Of Fungal Acne?
Consider the following steps to get rid of fungal acne effectively:
- Use topical antifungal treatments, such as creams or gels containing ketoconazole or pyrithione zinc.
- Keep the affected area clean and dry; avoid using comedogenic products; and make dietary adjustments to reduce yeast-promoting foods.
- Visit your dermatologist for personalised suggestions and treatment.
How Does Fungal Acne Start?
Fungal acne starts when there is an overgrowth of the fungus Malassezia on the skin. This overgrowth is triggered by excessive moisture, humidity, oily skin, certain skincare products, and a weakened immune system. The fungus infects the hair follicles, leading to the development of fungal acne.
What Kills Fungal Acne Fast?
To effectively kill fungal acne fast, you can use antifungal treatments such as topical creams containing ingredients like ketoconazole or pyrithione zinc. Doctors may prescribe Oral antifungal medications for severe cases. Consistent use of these treatments and good hygiene practices can help quickly eliminate fungal acne.
Is Aloe Vera Good For Fungal Acne?
Aloe vera can help alleviate redness and irritation associated with acne, but it is not explicitly designed to kill the fungus causing fungal acne. While aloe vera has soothing and anti-inflammatory properties, it may not directly treat fungal acne. Antifungal treatments are typically more effective for treating this condition.
How Do You Permanently Treat Fungal Infections?
Permanently treating fungal infections requires a comprehensive approach. Use antifungal medications, both topical and oral, as prescribed by a healthcare professional. Practise good hygiene, keep the affected area clean and dry, avoid sharing personal items, wear breathable fabrics, and maintain a healthy lifestyle. Make it a routine to do a follow-up check with your healthcare provider.
Does Salicylic Acid Help Fungal Acne?
Salicylic acid is primarily effective against acne caused by bacteria and excess oil rather than fungal acne. While it may help with exfoliation and unclogging pores, it is not explicitly designed to target the fungus-causing fungal acne. Antifungal treatments are generally more effective for treating this condition.
What Triggers Fungal Acne On Face?
Fungal acne on the face grows by factors such as excessive moisture, humidity, oily skin, wearing occlusive makeup or tight clothing, using certain skincare products that promote fungal growth, and having a weakened immune system.